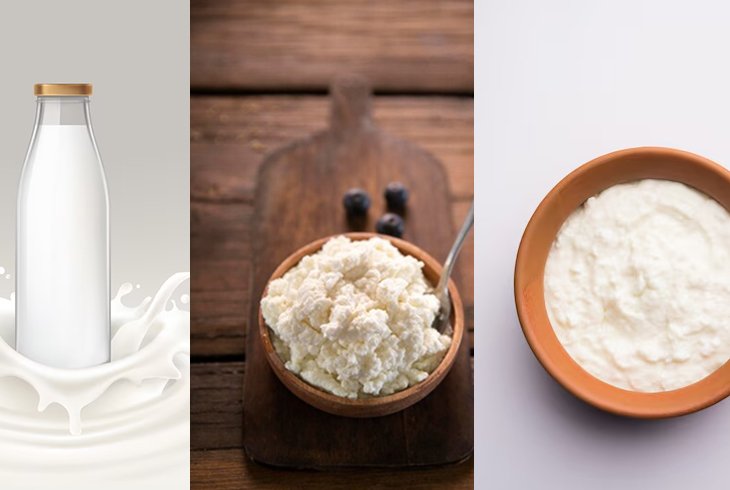
For dairy lovers, deciding between milk, paneer, and curd can be tricky. Each of these dairy products offers unique health benefits depending on your nutritional needs, dietary preferences, and any restrictions you may have. Let's break down the key differences and advantages to help you choose the best option for your diet.
Milk: The
Bone Builder
Milk is
often considered a cornerstone of a healthy diet due to its rich nutrient
profile. It supports bone health and can help maintain healthy blood pressure
due to its potassium content.
Nutritional
Benefits:
- A 250 ml
serving of fat-free milk contains 90 calories and 9 grams of protein.
- It also
provides 8% of the daily recommended value of vitamin B12, 2% of
vitamin A, and 12% of calcium.
- Milk is also
rich in magnesium, potassium, and sodium.
According to
Ayurveda, milk is highly nourishing when digested properly, balancing emotions
and supporting overall vitality. To aid digestion, it's advised to drink warm
milk rather than cold, as heating it enhances digestibility and reduces its
"kapha" properties, making it lighter on the stomach.
Paneer:
The Protein Powerhouse
Paneer, or
Indian cottage cheese, is packed with protein and essential nutrients, making
it a great choice for those focused on muscle building, digestion, and immune
support.
Nutritional
Benefits:
- A 100g
serving of paneer provides 321 calories, 25 grams of protein, 25
grams of fat, and just 3.57 grams of carbohydrates.
- Rich in
protein, paneer is an excellent choice for vegetarians and those on low-carb or
high-protein diets.
Paneer is
especially beneficial for those looking to support muscle growth and repair,
making it an ideal option for athletes and fitness enthusiasts. It’s also easy
to incorporate into meals and can be enjoyed in a variety of dishes.
Curd: The
Gut-Friendly Dairy
Curd, or
yogurt, is known for its digestive benefits. Thanks to its probiotic content,
curd promotes a healthy gut microbiome, improves digestion, and boosts
immunity. It's often easier to digest than milk and keeps you feeling full for
longer.
Nutritional
Benefits:
- A cup of
fat-free curd typically contains 98 calories and 11 grams of protein.
- Like milk,
curd is a good source of vitamin B12 (8% of the daily requirement),
vitamin A (2%), and calcium (8%).
- It also
provides moderate amounts of magnesium, potassium, and sodium.
Curd is
particularly beneficial for gut health due to its probiotic bacteria, which
help cleanse the digestive tract and protect against infections. However,
Ayurveda recommends that curd should not be consumed daily or at night, as it
can increase inflammation in the body, aggravating the kapha and pitta
doshas.
Which
Dairy Product Should You Choose?
Though all
three dairy products offer valuable nutrients, they are best consumed in
moderation and according to your specific health needs:
- For Bone
Health: Both milk
and curd are excellent choices due to their high calcium and vitamin D content.
- For
Muscle Building:
Paneer and milk are superior sources of protein, which supports muscle growth
and repair.
- For Gut
Health: Curd, with
its probiotic content, is the best choice to support digestive health.
- For
Lactose Intolerance:
Curd tends to be better tolerated by those with lactose sensitivity, though
lactose-free milk options are available. Paneer is also a good choice since it
contains minimal lactose.
Recommended Consumption
To reap the
benefits of each dairy product without overconsuming any one type:
- Milk: Best consumed daily, if you're not
lactose intolerant.
- Paneer: Ideal to include once a week as a
high-protein, nutrient-dense option.
- Curd: Consume 2-3 times a week, keeping
in mind Ayurveda’s advice to avoid daily or nighttime consumption, especially
if you have a tendency toward inflammation or bleeding disorders.
Incorporating
a variety of dairy products into your diet can provide a well-rounded intake of
essential nutrients. So, whether you're looking to boost your bone health,
muscle growth, or gut health, each of these dairy products has something
valuable to offer.